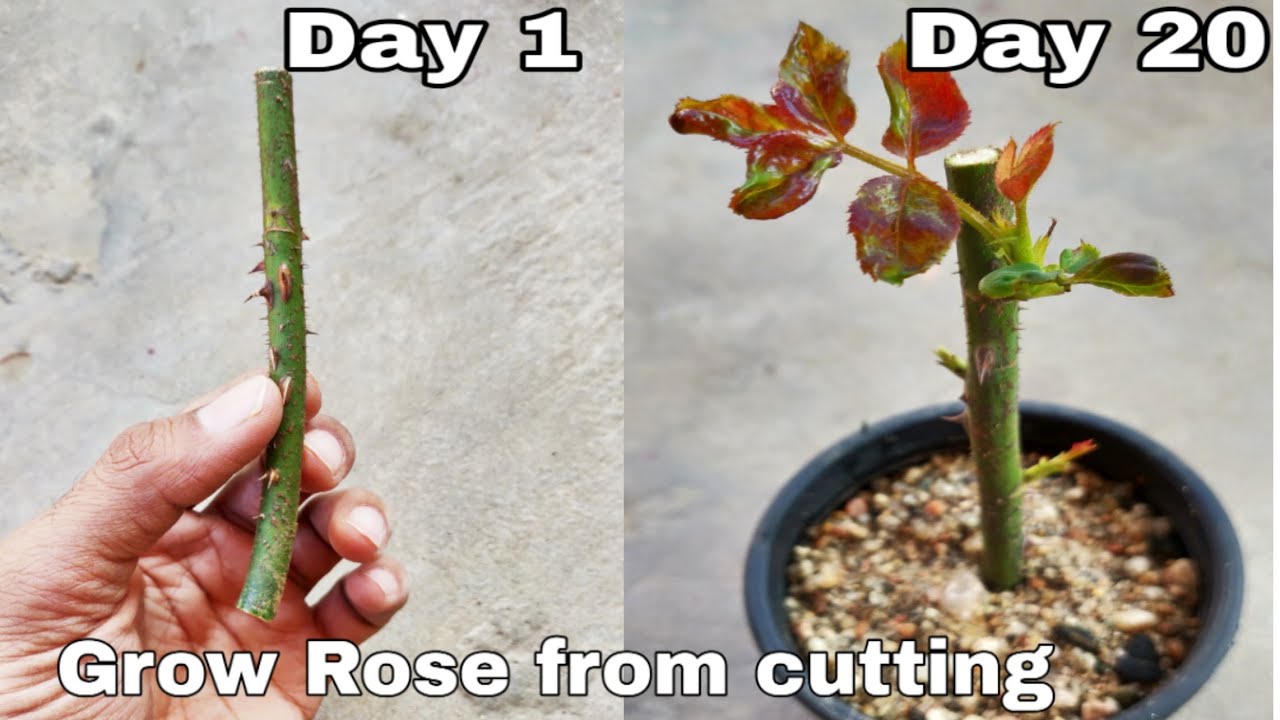
Grow Your Perfect Rose Garden: How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings Successfully – a title that promises a beautiful and rewarding journey. Imagine transforming a single rose cutting into a flourishing bush, a testament to your green thumb and a source of pride in your garden.
This is the magic of rose propagation, a technique that allows you to expand your rose collection, preserve cherished varieties, and experience the joy of nurturing life from a simple stem.
Rose propagation from cuttings is a surprisingly accessible and fulfilling endeavor. It’s not just about saving money on new plants; it’s about connecting with the natural world and witnessing the transformative power of growth. From choosing the right cuttings to nurturing them into strong, blooming bushes, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to create a rose garden that reflects your personal touch and passion.
The Allure of Rose Propagation
Rose propagation from cuttings offers a rewarding and cost-effective way to expand your rose garden. By taking cuttings from your existing rose bushes, you can create new plants that are genetically identical to the parent, preserving the beauty and unique characteristics of your favorite varieties.
The Benefits of Propagating Roses from Cuttings
Propagating roses from cuttings offers several advantages, making it an appealing choice for rose enthusiasts.
- Cost-Effectiveness:Purchasing new rose bushes can be expensive, especially if you want to add several new varieties to your garden. Propagating roses from cuttings allows you to create new plants for a fraction of the cost, making it a budget-friendly way to expand your collection.
- Preservation of Desired Varieties:Rose propagation from cuttings ensures that the new plants inherit the same genetic makeup as the parent plant, preserving the unique characteristics, such as flower color, fragrance, and disease resistance. This allows you to maintain your favorite varieties and enjoy their beauty for years to come.
Growing your own rose garden from cuttings can be a rewarding experience, but it requires some knowledge and patience. You’ll need to select the right type of cuttings, prepare them properly, and provide them with the ideal conditions for rooting.
To ensure success, it’s crucial to understand the best techniques for propagating roses from cuttings. The Best Techniques for Propagating Roses From Cuttings: A Comprehensive Guide offers a detailed exploration of these methods, covering everything from selecting the right time of year to using rooting hormones.
By mastering these techniques, you can increase your chances of success and enjoy the beauty of your own rose garden.
- A Rewarding Experience:Nurturing a rose garden from cuttings provides a sense of accomplishment and satisfaction. Witnessing the cuttings develop roots and eventually bloom into beautiful roses is a rewarding experience that deepens your connection with your garden.
Selecting the Right Cuttings
Choosing the right rose cuttings is crucial for successful propagation. Selecting healthy and vigorous cuttings from the current year’s growth will significantly increase your chances of success.
Time of Year for Taking Cuttings
The ideal time to take rose cuttings is during the active growing season when the plant is producing new growth. This period typically falls between late spring and early summer, when the rose bushes are in full bloom.
- Spring:The ideal time for taking cuttings is in the spring after the last frost. The new growth is soft and pliable, making it easier to root.
- Summer:Summer cuttings can also be successful, but the wood may be harder and require longer to root. It is important to take cuttings from the current year’s growth.
- Fall:Taking cuttings in the fall is not recommended as the plant is preparing for dormancy and the cuttings may not root successfully.
Choosing Healthy and Vigorous Cuttings
It is important to select healthy and vigorous cuttings from the current year’s growth. These cuttings are more likely to root successfully.
- Select stems from the current year’s growth:This is the most important factor in choosing successful cuttings. New growth is soft and pliable, making it easier to root. Look for stems that are green and have not yet hardened.
- Choose stems that are about 6-8 inches long:This length provides enough surface area for the cuttings to root. Cuttings that are too short may not have enough energy reserves to root.
- Avoid stems that are diseased or damaged:Damaged or diseased stems are more likely to fail to root. Look for stems that are free of pests, diseases, and blemishes.
Preparing the Cuttings

Once you’ve selected your ideal rose cuttings, it’s time to prepare them for propagation. Proper preparation is crucial for successful rooting, ensuring your cuttings have the best chance of developing strong roots and thriving in their new home.
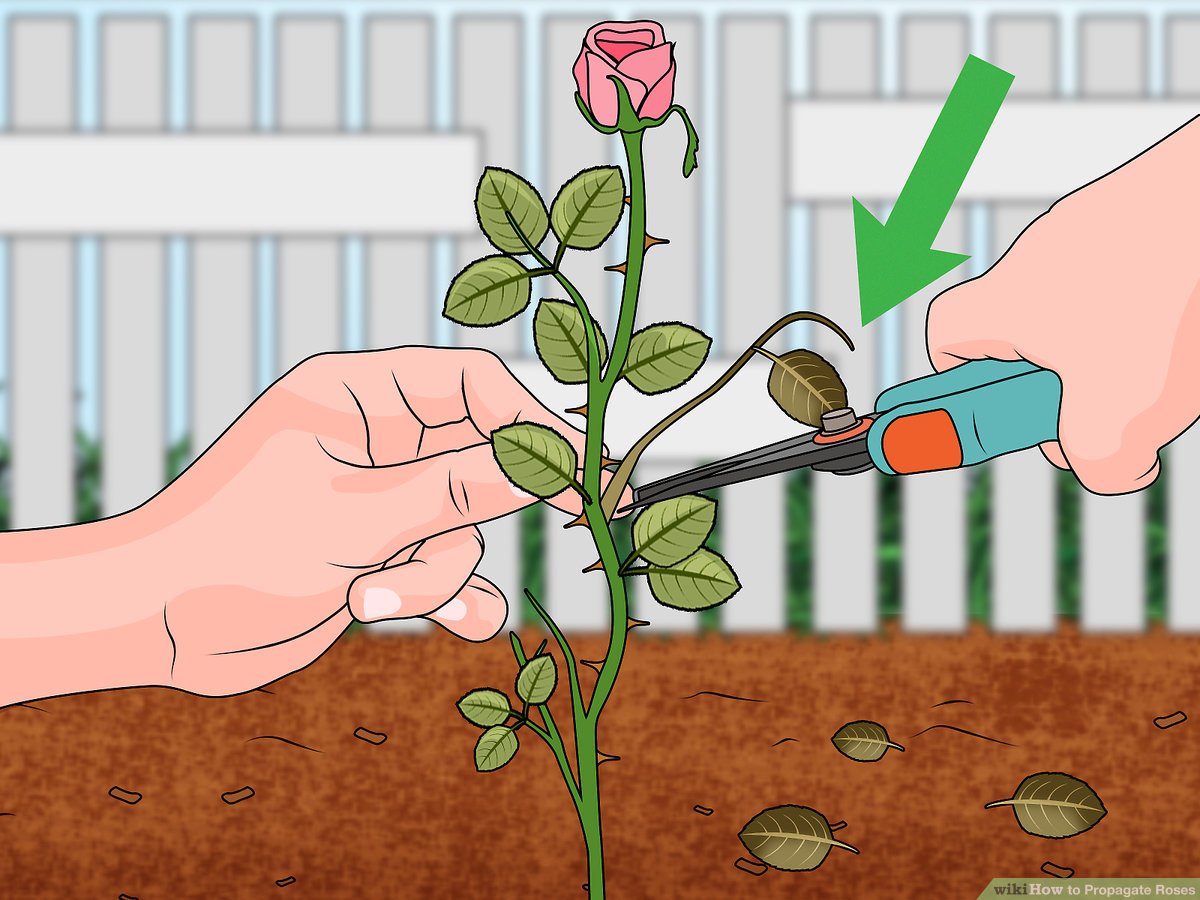
Making Clean Cuts
Using sharp, clean tools is paramount for preparing rose cuttings. Dull tools can crush the stem, hindering root development. Clean tools prevent the transmission of diseases that can harm your cuttings.
- Use a sharp, clean knife or pruning shears:A sharp blade ensures a clean cut, minimizing damage to the stem.
- Sterilize your tools before use:Wipe your tools with rubbing alcohol or a diluted bleach solution to eliminate any harmful bacteria or fungi.
- Make a diagonal cut just below a node:Nodes are the points on the stem where leaves emerge. Cutting just below a node encourages root growth from the node.
Removing Leaves from the Lower Portion, Grow Your Perfect Rose Garden: How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings Successfully
Removing leaves from the lower portion of the cutting promotes root development. Leaves draw energy from the stem, and by removing them, you direct that energy towards root growth.
Growing your own roses from cuttings is a rewarding and cost-effective way to expand your rose garden. This technique allows you to multiply your favorite varieties and create a stunning display of blooms. For a comprehensive guide on the process, check out From Garden to Glory: How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings for a Vibrant Display , which provides detailed instructions and tips for success.
With a little patience and care, you can easily propagate your own rose bushes and enjoy their beauty for years to come.
- Remove all leaves below the soil line:This prevents rot and ensures that energy is directed towards root development.
- Pinch off any remaining leaves above the soil line:You can leave a few leaves at the top of the cutting to help with photosynthesis.
Treating Cuttings with Rooting Hormone
Rooting hormone is a beneficial tool that can significantly boost the success rate of rose propagation. It contains plant hormones that stimulate root growth, encouraging the cutting to develop a robust root system.
- Choose a rooting hormone powder or liquid:Both types are effective, and the choice depends on personal preference.
- Dip the cut end of the cutting into the rooting hormone:Follow the instructions on the product label for the correct application method.
- Apply rooting hormone sparingly:Too much hormone can inhibit root development, so use it judiciously.
Rooting Methods: Grow Your Perfect Rose Garden: How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings Successfully
Once your cuttings are prepared, it’s time to focus on the crucial step of rooting them. Several methods are available, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these methods allows you to choose the one that best suits your needs and resources.
Water Propagation
Water propagation is a simple and straightforward method that allows you to observe root development closely. It involves placing the prepared cuttings in a clear glass or container filled with clean water.
- Advantages:Water propagation offers a visual advantage, enabling you to monitor root growth and ensure the cutting remains hydrated. It’s also a relatively inexpensive method requiring minimal supplies.
- Disadvantages:This method can lead to root rot if the water isn’t changed regularly. The roots may also be fragile and prone to damage when transferred to soil. Furthermore, water propagation may not be suitable for all rose varieties.
Soil Propagation
Soil propagation is the most common method for rooting rose cuttings. It involves planting the prepared cuttings directly into a suitable rooting medium.
- Advantages:This method provides a stable environment for root development and encourages stronger root growth compared to water propagation. It also allows the cuttings to acclimate to the soil environment before transplanting.
- Disadvantages:Soil propagation requires more care and attention to maintain the appropriate moisture levels and prevent fungal infections. The process can also be more time-consuming than water propagation.
Rooting Medium
A rooting medium is a specific type of soil or mixture designed to promote root growth.
- Advantages:Rooting mediums are formulated to provide optimal drainage, aeration, and moisture retention, creating an ideal environment for root development. They are also typically sterile, reducing the risk of fungal infections.
- Disadvantages:Rooting mediums can be more expensive than regular potting soil. It’s essential to choose the right type of rooting medium for your rose variety and climate.
Caring for Rooted Cuttings
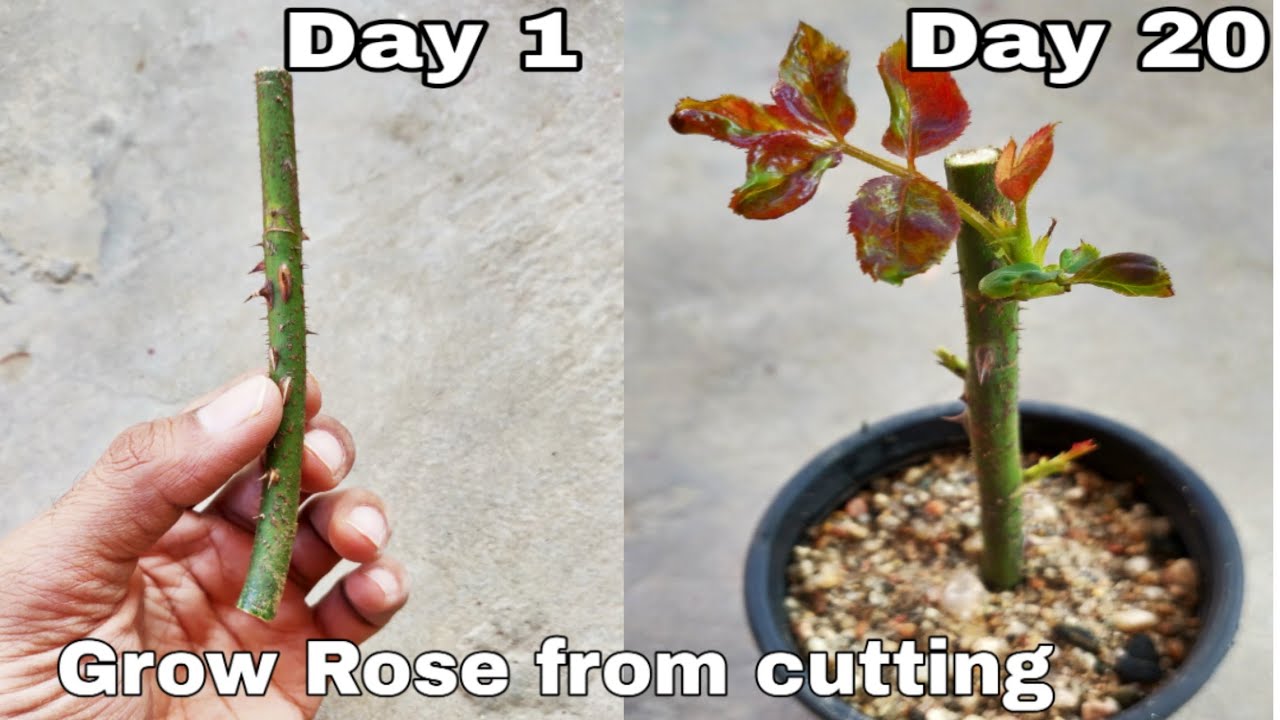

The transition from rooting medium to a more permanent environment is crucial for newly rooted rose cuttings. Proper care during this stage ensures their survival and promotes vigorous growth.
Watering
Watering newly rooted rose cuttings is a delicate balance. They need moisture to thrive but are also susceptible to root rot if overwatered.
- Check the soil moisture:Before watering, check the soil moisture by inserting a finger about an inch deep. If the soil feels dry, it’s time to water.
- Water thoroughly:When watering, apply water until it drains from the bottom of the pot. This ensures the entire root system is moistened.
- Avoid overwatering:Allow the soil to dry slightly between waterings. Overwatering can lead to root rot, which can be fatal to young plants.
Light Exposure
Sunlight is essential for photosynthesis, but newly rooted rose cuttings are sensitive to intense sunlight.
- Gradually acclimate to sunlight:Start by placing the cuttings in a shaded location, gradually increasing their exposure to direct sunlight over several weeks.
- Provide bright, indirect light:Ideally, they should receive bright, indirect light for several hours daily. This will encourage healthy growth without scorching their delicate leaves.
- Avoid midday sun:Avoid exposing the cuttings to intense midday sun, especially during hot summer months, as this can lead to wilting and leaf burn.
Protecting from Pests and Diseases
Newly rooted rose cuttings are more vulnerable to pests and diseases than established plants.
- Regularly inspect for pests:Inspect the cuttings regularly for signs of pests, such as aphids, spider mites, or whiteflies.
- Use insecticidal soap or neem oil:If pests are present, treat them with an insecticidal soap or neem oil spray.
- Maintain good sanitation:Remove any diseased or damaged leaves promptly to prevent the spread of diseases.
Transplanting Rooted Cuttings
Once the rooted cuttings have developed a strong root system, it’s time to transplant them into individual pots or directly into the garden.
- Prepare the new location:Prepare the new planting site by amending the soil with compost or other organic matter to improve drainage and fertility.
- Dig a hole:Dig a hole that is slightly larger than the root ball of the cutting.
- Gently remove the cutting from the rooting medium:Gently remove the cutting from its rooting medium, being careful not to damage the roots.
- Place the cutting in the hole:Place the cutting in the hole, ensuring the root ball is level with the soil surface.
- Backfill the hole:Backfill the hole with soil, gently firming it around the roots.
- Water thoroughly:Water the newly transplanted cutting thoroughly to settle the soil and ensure good root contact.
Hardening Off
Hardening off is a process that gradually acclimates newly rooted cuttings to outdoor conditions.
- Gradually increase exposure:Start by placing the cuttings in a sheltered location for a few hours each day, gradually increasing the duration of exposure over several days.
- Protect from harsh conditions:Protect the cuttings from strong winds, extreme temperatures, and heavy rainfall during the hardening off process.
- Monitor for signs of stress:Monitor the cuttings for signs of stress, such as wilting or leaf drop. If you notice any stress, reduce the exposure time or provide additional shade.
Cultivating Your Rose Garden
After successfully propagating your rose cuttings, the next step is to nurture them into thriving rose bushes. This involves providing them with the right conditions and care practices to ensure optimal growth and blooming.
Rose Bush Care Practices
A well-maintained rose garden is the result of consistent care. Here’s a table outlining essential practices:
Watering Requirements |
Fertilizing Needs |
Pruning Techniques |
Pest and Disease Management |
|---|---|---|---|
Water deeply and infrequently, ensuring the soil is moist but not waterlogged. |
Fertilize regularly with a balanced fertilizer specifically formulated for roses. |
Prune regularly to promote healthy growth and flowering. Remove dead, diseased, or crossing branches. |
Inspect your roses regularly for signs of pests or diseases. Treat promptly with appropriate methods. |
Ensuring Optimal Growth and Blooming
Here are some tips to promote healthy growth and abundant blooms in your rose garden:
- Choose the right location:Roses thrive in full sun, receiving at least six hours of direct sunlight daily. Select a location with well-drained soil and good air circulation.
- Mulch around your roses:Applying a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or shredded bark, helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
- Deadhead spent blooms:Regularly remove faded flowers to encourage new blooms and prevent the formation of rose hips.
- Protect your roses from harsh weather:Provide shelter from strong winds and heavy rainfall, especially during winter. In colder climates, consider winter protection measures like wrapping the base of the plant with burlap or straw.
Ultimate Conclusion
With patience, care, and a little bit of horticultural know-how, you can turn a simple rose cutting into a thriving addition to your garden. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a novice enthusiast, the journey of propagating roses is a rewarding experience that will bring beauty, fragrance, and a sense of accomplishment to your green space.
So, grab your sharp shears, choose your favorite rose varieties, and embark on the exciting adventure of creating your perfect rose garden, one cutting at a time.
Top FAQs
What are the best types of roses for propagation from cuttings?
Hybrid tea roses, floribunda roses, and grandiflora roses are generally considered good choices for propagation from cuttings. They tend to root more easily than some other types of roses.
How long does it take for rose cuttings to root?
Rooting time can vary depending on the rose variety, the rooting method, and environmental factors. Generally, it can take anywhere from 4 to 8 weeks for rose cuttings to develop roots.
Can I propagate roses from cuttings taken from a store-bought rose?
Yes, you can! Just make sure the rose was not treated with growth regulators that might inhibit rooting.
